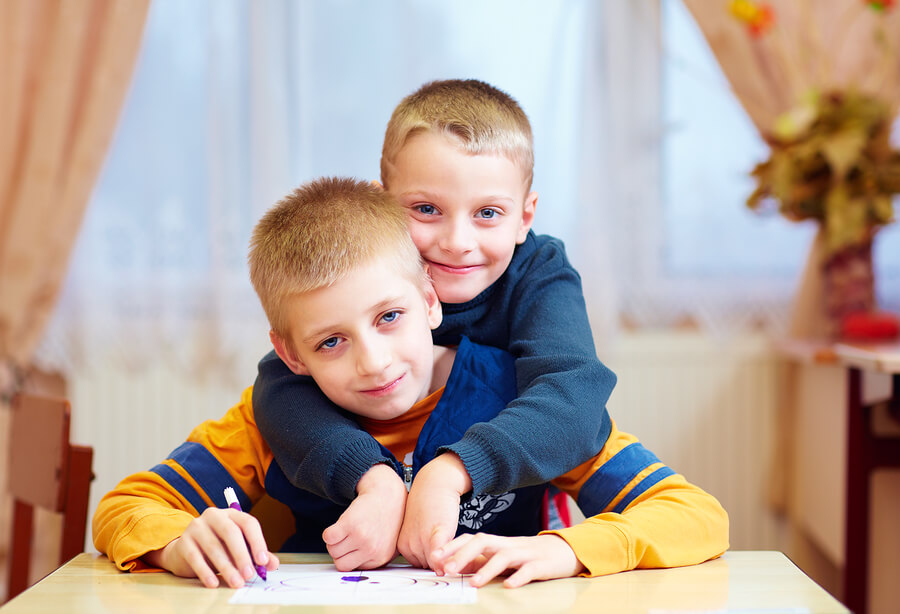
Autism is a neurodevelopmental spectrum disorder that typically appears in the first three years of a child’s life. “Spectrum” indicates that different people have varying degrees of severity. Autism is unique to each person, and each person has their own set of symptoms, difficulties, and treatments. They also have their own set of abilities and strengths.
Diagnosis & Early Intervention
Characterization and diagnosis of Autism has been clarified over the years. Previously, Asperger’s Syndrome and PDD-NOS fell under different branches of developmental disorders as Autism; although, the DSM-5 no longer diagnoses them as separate disorders and instead recognizes them as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). People with ASD may exhibit a wide range of symptoms including, but not limited to, sensory sensitivities, seizures, GI problems, reduced facial expressions and eye contact, repetitive behaviors, and difficulty recognizing their own and others’ emotions. They may also struggle with mental health such as anxiety and attention challenges.
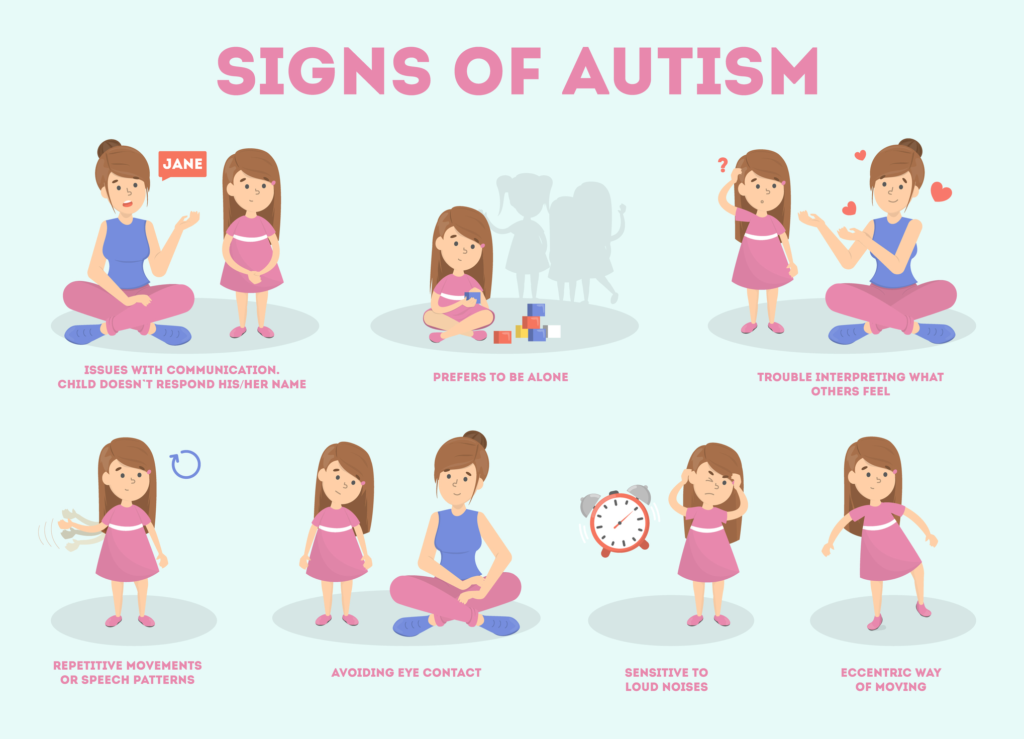
Approximately 1 in 44 children are diagnosed with ASD. Autism can be a minor challenge for some, but for others, it can cause significant interference with day-to-day life and both mental and physical wellbeing. For many, it’s diagnosed early, possibly as early as 18 months of age. However, symptoms can go unrecognized, causing critical delays in treatment and intervention. Diagnosing ASD early can prove to be extremely beneficial by leading to greater positive outcomes for later in life.
New Test Using Hair Strand
Novel treatments for ASD are beginning to show more innovation and promise. Researchers have developed a new diagnosis test for Autism that can find risk factors using merely a single strand of hair. This test, sponsored by LinusBio, is still in its beginning stages of development, and it shouldn’t be the main or only source of diagnosis/treatment for ASD. Intead, it should be used as a supporting piece in a larger puzzle.
This new test is the first of its kind, and it hopes to diagnose Autism before symptoms appear, expediting the treatment process. In many cases, ASD is diagnosed at age 4, by which a significant amount of brain development has already occurred. Analysis of results show that nearly 81% of Autism cases were predicted correctly using this test. This test’s technology was created through research at Mount Sinai. It analyzes a single strand of hair from an infant, which can generate a spotlight on growing conditions and exposures during pregnancy, especially the third trimester, which is a critical period for human development.
Similar to how a tree’s rings or a person’s scars can be a lens into specific timelines of growth, a mere centimeter of an infant’s hair encapsulates a month’s worth of vital developmental information. The hair strand is transformed into plasma for data gathering and analysis using a laser. The test collects metal exposure and metabolism data in 4-6 hour additions, creating large quantities of data that can be organized using computer algorithms. Metal metabolism irregularities then act as biomarkers for possible ASD progression.
With further testing, refinement, and repetitions, this test could prove to be extremely beneficial for ASD intervention treatment in the future. The test acts as a gateway for more innovative and more efficient diagnostic techniques. It’s only one step in a bigger journey to spot Autism early and ensure a person gets the best possible treatment possible.


